Traditional motion detection often floods security systems with false alarms, wasting time and resources. Smart Motion Detection (SMD) offers a breakthrough, especially for PTZ cameras, enhancing accuracy and reducing unnecessary alerts effectively.
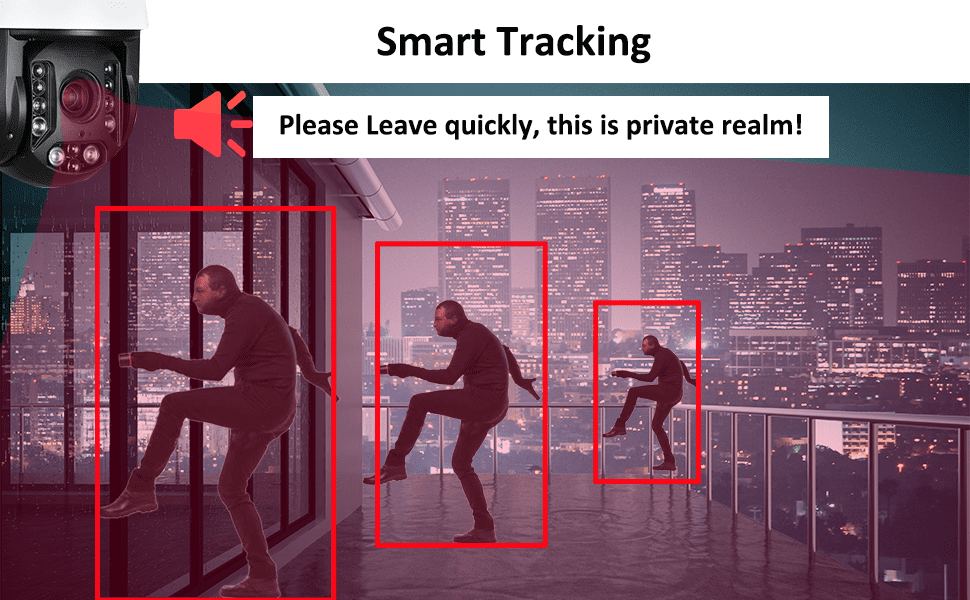
Smart Motion Detection for PTZ cameras uses AI algorithms to identify humans and vehicles, significantly minimizing false alarms compared to traditional pixel-based methods. It integrates with PTZ features, adjusts with camera movement, and enables precise alerts tailored for dynamic surveillance environments.
Dive deeper to explore how SMD evolved through versions like SMD+, 3.0, and 4.0, practical setup guides for PTZ cameras and NVRs, tips to reduce false positives, and the interplay between AI detection and PTZ functionality for optimized monitoring.
Understanding Smart Motion Detection (SMD) Technology for PTZ Cameras
Smart Motion Detection (SMD) technology represents an advanced leap in motion detection systems designed for PTZ cameras (Pan-Tilt-Zoom). By harnessing AI, SMD provides a significant edge over traditional systems, accurately discerning human and vehicle movements from general activity. Let’s dive into its key features and evolutions.
What is Smart Motion Detection and How it Differs from Traditional Motion Detection
Smart Motion Detection (SMD) leverages artificial intelligence to identify patterns specifically related to humans and vehicles. Unlike traditional motion detection that relies on pixel-level changes to trigger alarms, SMD minimizes false positives by applying AI algorithms that distinguish relevant activity from noise, like environmental movements or lighting variations.
Key differences include: – Traditional Motion Detection: Pixel-based triggers often misinterpret changes such as shadows, raindrops, or wind-blown leaves as meaningful movements. – SMD’s AI Approach: Recognizes defined shapes (humans and vehicles), ensuring alerts are more accurate and contextually relevant.
The benefits? Reduced false alarms, leading to more reliable notifications and less frustration for users managing surveillance systems.
Evolution and Versions of SMD (SMD+, 3.0, 4.0)
Smart Motion Detection has evolved through several iterations, each improving accuracy and reliability for PTZ cameras:
- SMD+: Boasts an approximate 98% accuracy rate. It represents a key advancement by noticeably reducing false alarms caused by objects such as animals or blowing debris.
- SMD 3.0: Delivers even greater accuracy, reaching 99%. This version further minimizes disturbances caused by small animals, making surveillance more efficient.
- SMD 4.0: Currently the pinnacle of SMD technology, it offers the highest precision and lowest rates of false positives, ensuring utmost confidence in security monitoring.
Each version significantly enhances surveillance reliability, with PTZ cameras becoming vital tools for proactive and effective security measures.
How AI Detects Humans and Vehicles to Reduce False Positives
AI in SMD operates by analyzing video frames to classify objects within them. Sophisticated algorithms delve into factors like object shape, size, and movement patterns. For instance:
- Human Detection: Identifies signature body shapes and typical motion patterns unique to humans.
- Vehicle Detection: Recognizes specific contours and structural details of cars, trucks, and other vehicles.
This targeted analysis ensures movements from irrelevant sources (e.g., leaves or shifting shadows) are ignored. However, limitations include scenarios where a large animal may still trigger a false positive, although these instances are increasingly rare thanks to continued AI refinement.
Differences Between SMD and Other AI-based Detection Systems like IVS
While SMD focuses primarily on identifying humans and vehicles, Intelligent Video Systems (IVS) employ a broader set of analytical rules (e.g., line crossing, intrusion zones). The key distinctions include:
- SMD: Ideal for general surveillance where human and vehicle detection is critical, minimizing unnecessary alerts.
- IVS: Designed for specific rule-based detections, such as monitoring restricted access areas or counting entries and exits.
Both technologies can operate together, with SMD enriching IVS setups by overlaying its detection capabilities on traditional configurations. Knowing when to use each ensures a tailored and efficient approach to security.
Motion Detection Mechanics and Integration with PTZ Camera Features
Smart motion detection (SMD) adds significant intelligence to PTZ cameras, enhancing their ability to identify and track motion efficiently. This section explores how motion detection integrates with PTZ camera features, its interaction with SMD, and the underlying mechanics of sensor technology, along with addressing common challenges.
How Motion Detection Works in PTZ Cameras
Motion detection in PTZ cameras revolves around continuous video frame analysis, wherein the system monitors frames to detect pixel changes between sequential images. This process is essential for flagging motion within the camera’s field of view.
However, PTZ cameras face unique limitations due to their mobility. For example:
- Motion detection is disabled when the camera moves between preset positions, avoiding false alarms caused by motion blur.
- PTZ’s auto-patrolling behavior may delay the re-enabling of motion detection, as the camera must stabilize before resuming monitoring.
Despite these challenges, the balance between mobility and detection accuracy is well-designed for most applications.
Interaction Between SMD and PTZ Camera Movements
Smart Motion Detection (SMD) operates as an advanced complement to traditional motion detection. While it’s independent of preset and motion detection zones, enabling the base motion detection feature is crucial for SMD to function properly.
Key points to consider include:
- SMD uses AI algorithms to identify specific triggers such as humans and vehicles, irrespective of PTZ camera movements.
- Traditional motion detection acts as a foundation, ensuring reliable event monitoring when cameras are stationary or tracking.
- Practical adjustments like aligning SMD with PTZ’s auto-tracking ensure optimized detection even during complex camera movements.
This synchronization allows SMD to enhance event accuracy while minimizing false positives.
Role of Camera Sensors and Photodiodes in Motion Detection Reliability
At the heart of motion detection is the camera’s sensor technology, particularly photodiode arrays and associated electronics. These components are responsible for detecting variations in light and motion.
- Photodiodes capture light changes in the environment, which are analyzed to detect motion events.
- Advanced sensor technology reduces noise, improving reliability even in low-light conditions.
- The captured sensor data undergoes digital processing, converting raw information into actionable detection events, which may then trigger alarms or tracking features.
The choice of sensor technology is critical for achieving high accuracy and minimal false alarms.
Common Misunderstandings and Challenges
Motion detection for PTZ cameras is often misunderstood, leading to avoidable issues. Common pitfalls include: – Relying solely on motion detection, which can generate false alarms due to environmental changes like shadows or weather. – Misconceptions about SMD: it does not replace the traditional motion detection system but enhances it with AI-based filtering for specific objects. – Sensitivity and detection zones often confuse users, as improper settings can lead to missed or excessive alerts.
Users can mitigate these issues by understanding the layered approach that combines traditional motion detection with SMD, ensuring accurate and efficient performance in dynamic environments.
Setting Up and Configuring Smart Motion Detection on PTZ Cameras and NVR Systems
Smart Motion Detection (SMD) is a game-changing feature to maximize the effectiveness of PTZ cameras and NVR systems. It ensures targeted detections while reducing false alerts, but proper setup and tuning are essential for optimal performance. Here’s a detailed guide to configure SMD step by step.
Step-by-Step Setup via Monitor or TV Interface
To configure SMD via a monitor, start by accessing the NVR’s main menu. From there:
- Enable SMD: Locate the AI parameters menu and toggle the SMD feature on.
- Choose Detection Targets: Select whether you want the system to focus on humans, vehicles, or both, depending on your security needs.
- Adjust Sensitivity: Set sensitivity levels (Low, Medium, High) to balance between detection range and minimizing false positive alerts. Higher sensitivity usually means a wider detection range but may increase irrelevant triggers.
- Schedule Alerts: Configure detection schedules that align with activity patterns, and select event alert actions, such as notifications or video saving, to ensure timely responses.
These settings can be customized further as you observe how the system reacts to different scenarios.
Configuring SMD Through NVR Web Interface
If you prefer using the web interface, follow these steps:
- Login to the NVR: Enter the NVR IP address into your browser and log in using your credentials.
- Navigate to SMD Settings: Go to the AI > Parameters > SMD section where you can enable motion detection and adjust preferences.
- Set Sensitivity Levels: Tailor sensitivity adjustments to match environmental conditions like outdoor lighting changes or high-traffic zones.
- Save Changes: Always remember to save and apply your configurations before exiting to ensure they take effect.
This method offers the convenience of remote configuration from almost any device with a browser.
Practical Tips for Fine-Tuning Sensitivity and Reducing False Alarms
Optimizing sensitivity to avoid false alarms requires some best practices:
- Privacy Masks: Set up privacy masks to exclude motion-heavy areas, such as roads or trees swaying in the wind.
- Scheduled Detection: Use scheduling to limit monitoring to active periods such as evenings or business hours.
- Testing: Run live walkthroughs of the monitored area to test your settings and refine sensitivity based on the system’s live feedback.
Proactively applying these strategies improves the accuracy and reliability of motion detection.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While SMD is highly reliable, you may encounter a few common challenges:
- Disabled Detection During PTZ Movement: SMD pauses when the camera moves. Use fixed zones or plan motion monitoring around patrol periods.
- Confusion Over Sensitivity and Zones: Misunderstanding sensitivity can affect performance. Know that lower sensitivity levels prioritize key motion like human activity over minor movements.
- Trigger Verification: Confirm that the system records triggers properly even when general motion sensitivity is low. This ensures a focus on humans and vehicles as intended.
- Compatibility Checks: Make sure your camera and NVR firmware are updated and compatible to support the full suite of SMD features.
By addressing these issues promptly, you can maintain consistent performance and enjoy the full benefits of Smart Motion Detection.
Optimizing Smart Motion Detection for Enhanced Surveillance Performance
Enhancing surveillance performance requires more than just installing cameras. Smart Motion Detection (SMD) features can be fine-tuned to optimize accuracy, minimize disruptions, and ensure comprehensive coverage. In this section, we’ll explore strategies and techniques to achieve the best results from SMD systems.
Leveraging Privacy Masks and Scheduling for Performance Optimization
Privacy masks are a critical tool for modern surveillance systems. These allow users to block specific areas within the camera’s field of view where movement should not trigger detection. For example, you can use privacy masks to exclude irrelevant areas such as roads with constant vehicle movement, neighbor windows, or trees prone to swaying in wind. This approach not only respects privacy but also focuses resources on meaningful activity.
Similarly, scheduling motion detection during high-priority time periods reduces false alerts. For example, you can activate motion tracking only after business hours for office settings or at night for residential areas. This targeted scheduling helps maximize the efficiency of surveillance systems, minimizing distractions from irrelevant motion alerts during predictable low-risk periods.
Practical Testing and Calibration Techniques
Accurate Smart Motion Detection requires practical testing and regular calibration to optimize performance. Start by verifying motion detection capabilities through live testing – monitor how the system responds to controlled movements within the camera’s view. Take note of unnecessary activations or blind spots.
Fine-tune sensitivity levels and detection zones based on the specific environment. For instance, outdoor scenarios exposed to weather changes may benefit from medium sensitivity to avoid reacting to minor movements like leaves falling. Pair this with precise detection area selection to focus on entry doors, gates, or driveways.
Use live diagrams or feedback tools provided by your surveillance software to iteratively refine settings. These visual aids help track zones currently monitored and provide instant validation of changes during real-time environment adjustments.
Integrating SMD with Broader Surveillance Strategies
Smart Motion Detection becomes even more powerful when integrated into a broader surveillance workflow. One effective approach is combining SMD-triggered recording with alarm notifications. For instance, captured motion events can automatically send alerts directly to administrators, triggering actions like dispatching security teams.
Additionally, pairing SMD with auto-tracking PTZ camera features ensures dynamic event capture. When motion is detected, the camera can pivot, tilt, and zoom to follow moving subjects, offering a more expansive view of unfolding events.
For a robust security strategy, compare SMD with other AI-based detection triggers such as line-crossing analytics, intrusion detection, and face recognition. Each has unique strengths: for example, line-crossing is excellent for marking restricted zones, while face recognition adds advanced identity verification, making these AI features ideal complements to traditional motion detection.
Understanding how Smart Motion Detection enhances PTZ camera performance is key to upgrading your surveillance system’s accuracy and efficiency. By leveraging AI to distinguish humans and vehicles from irrelevant motion, SMD significantly cuts false alarms—a common issue in traditional pixel-based detection. Integrating SMD with PTZ features, along with careful configuration and calibration, ensures targeted alerts and reliable monitoring even during camera movements.
Mastering SMD setup, sensitivity tuning, and practical troubleshooting empowers you to optimize detection tailored to your environment. This not only improves security responses but also saves time and resources through smarter alert management. To deepen your expertise and maximize your system’s capabilities, explore manufacturer-specific guides, firmware updates, and advanced PTZ models with cutting-edge AI features.
Take the next step: refine your Smart Motion Detection setup today and transform your PTZ surveillance into a smarter, more effective security solution. Contact Us NOW!



